Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
CT Brain. Brainstem and cerebellum without evidence of focal lesions. Lateral ventricles of normal volume. Third and fourth ventricles in midline. Basal subarachnoid cisterns normal configuration. Focal abnormalities are not observed in the brain parenchyma. Adequate gray matter-white matter differentiation.

Brain Lobe Anatomy Mri
Normal cranial CT Scan of the head: brain, bones of cranium, sinuses of the face. Fully annotated brain CT - Normal anatomy of the head on a cross-sectional cranial CT Scan (axial, sagittal and coronal): brain, bones of skull, paranasal sinuses, vasculary territories, cranial base.

Brain and face CT interactive anatomy atlas eAnatomy
Normal Axial CT and MRI Anatomy . On CT and MR scans the brain has been briefly viewed in infratentorial and supratentorial sections, as described below. CT scans are performed with a 15- to 20-degree angulation to the canthomeatal line at 8-mm increments. MRI scans are generally obtained parallel to the AC-PC line in the axial plane, with 6-mm.

Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
Cerebral Computed Tomography (CT) Cerebral computed tomography (CT) is a radiographic procedure that uses X-rays to produce medical images of the head, including the brain, skull, sinuses, and eye sockets (1).. Through cerebral CT, radiographers see the patient's brain without the need for surgery. The procedure creates medical images of certain parts of the brain, including the cerebrum.
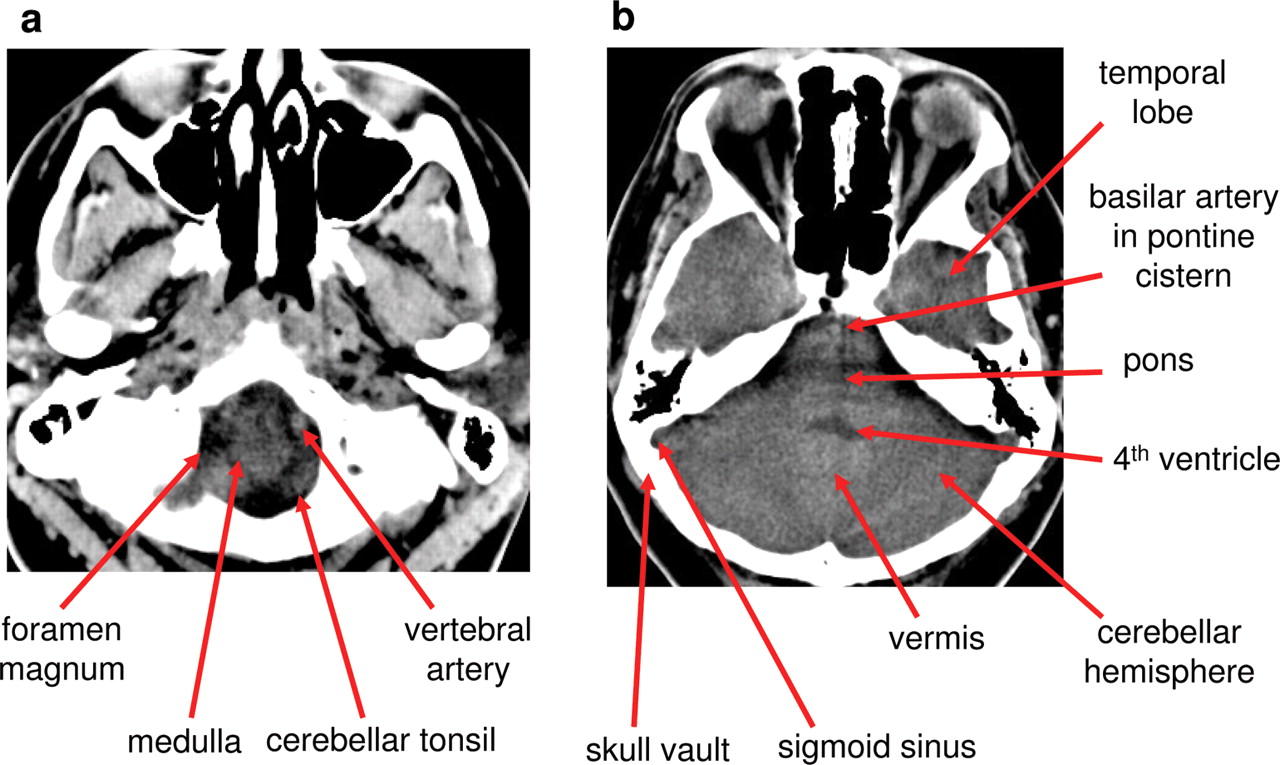
CT Brain Anatomy Posterior fossa
Neuroanatomy encompasses the anatomy of all structures of the: central nervous system (CNS), includes brain and spinal cord. peripheral nervous system (PNS) supporting tissues and structures. The functional description of neuroanatomy divides the nervous system into: somatic nervous system. autonomic nervous system.
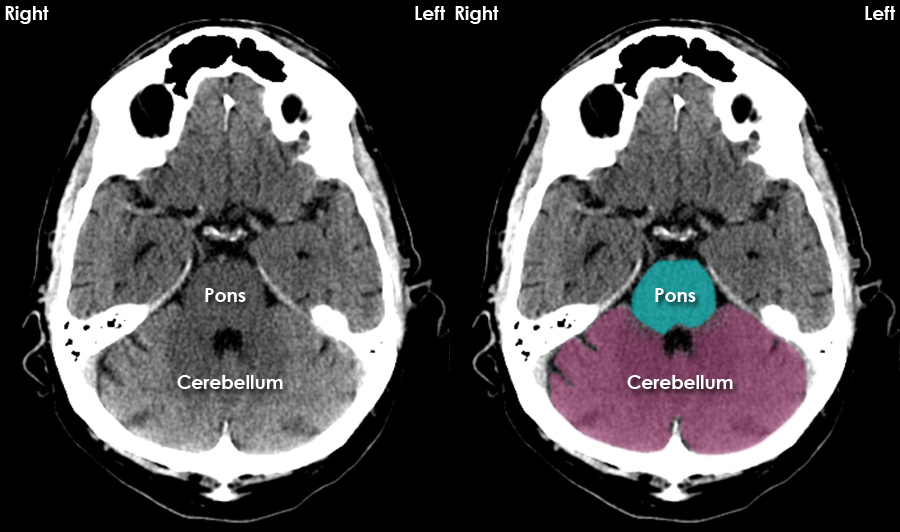
CT Brain Anatomy Tutorial introduction
Head CT Approach. First - evaluate normal anatomical structures, window for optimal brain tissue contrast Second - assess for signs of underlying pathology such as: mass effect, edema, midline shift, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, subdural or epidural collection/hematoma, or infarction Third - evaluate sinuses and osseous structures with bone.
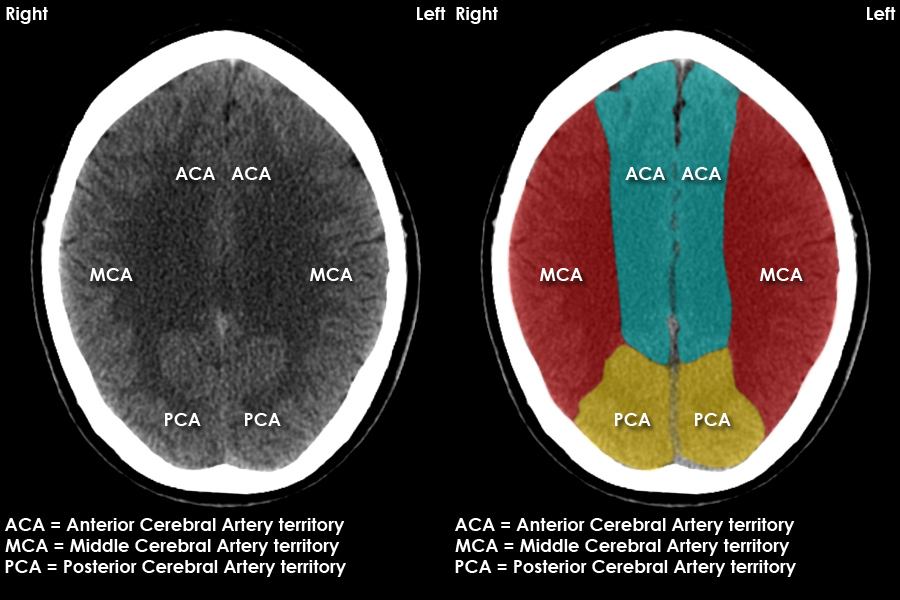
CT Brain Anatomy Cerebral vascular territories
Normal Anatomy of Brain (CT) by Kyaing Yi Mon Thin; 111 Normal anatomy by Mohamed shweel braın by HMB * CT Brain by Gourab Mitro Plaban; CT head by Mohit Kumar; Dr Abid cases by Abid Hussain; illustrations annotated images by Mini Singhal; CT Head Tutorial RadSIG by Alexander Troyer; NIMA by Miguel F Andrade Egues; 07 juillet by Amar Hadj; 07.
CT Head Normal Anatomy
CT Tutorials » CT Brain Anatomy ». Important grey matter structures visible on CT images of the brain include the cortex, insula, basal ganglia, and thalamus. Cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is a layer of grey matter formed in gyri (folds) over the entire brain surface.
brain cross sectional
Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31(4):767-770. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar; 2. Geibprasert S, Pongpech S, Jiarakongmun P, Shroff MM, Armstrong DC, Krings T. Radiologic assessment of brain arteriovenous malformations: what clinicians need to know.

Ct Scan Brain Anatomy Anatomy Of Head Ct Scan Normal The Brain On Ct And Mri / Frontal
Key points. White matter of the brain lies deep to the cortical grey matter. The internal capsules are white matter tracts which connect with the corona radiata and white matter of the cerebral hemispheres superiorly, and with the brain stem inferiorly. The corpus callosum is a white matter tract located in the midline.

Brain and face CT interactive anatomy atlas eAnatomy
CT brain introduction by Chris Bathurst Chichu study by Greeshma Reddy; NORMAL TC BRAIN by Bianca Jaqueline Escobar; NORMAL TC BRAIN by Bianca Jaqueline Escobar; EncefaloAnatomia by marcel de 2begin by David Fällmar; UQ Radiologic Anatomy 1. Brain 1.04 Cerebellum by Craig Hacking UQ Radiologic Anatomy 1. Brain 1.01 Cerebrum by Craig Hacking

MRI anatomy brain axial image 18 Brain anatomy, Mri brain, Ct brain anatomy
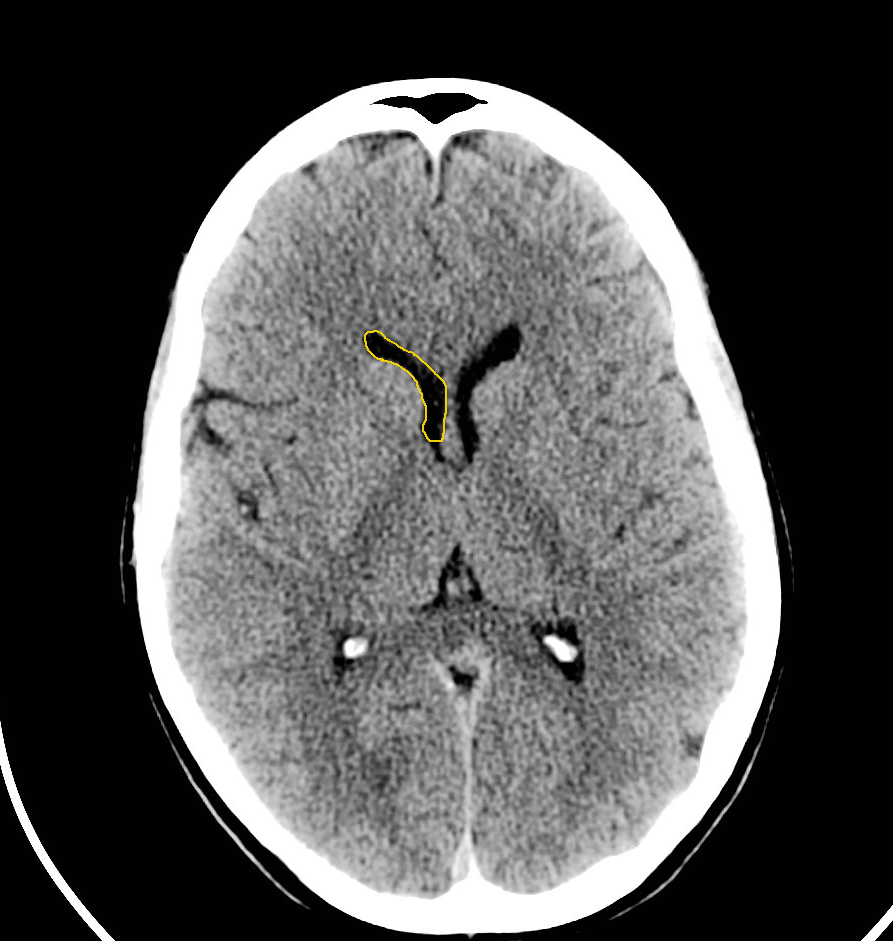
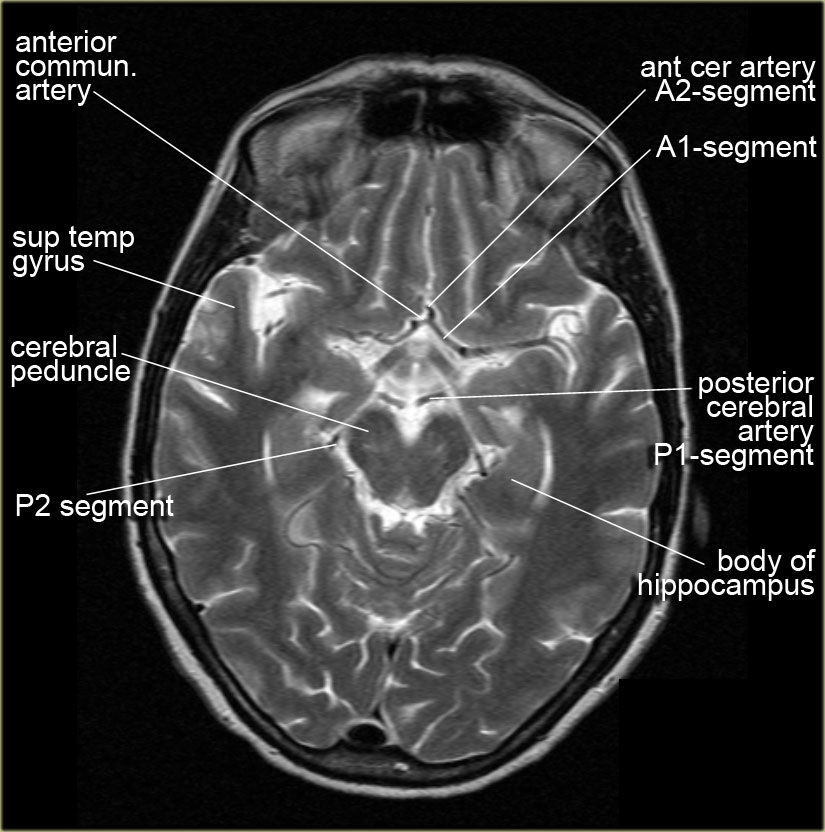
Also called ambient cistern is a cistern of the subarachnoid space between the posterior end of the corpus callosum and the superior surface of the cerebellum. It is sometimes defined as including the quadrigerminal cistern. On the left a coronal view of the segments of the middle cerebral artery. Horizontal M1-segment.

Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
Last updated: 29 June 2022. Basic radiological anatomy of the brain and spine with annotated CT and MRI images covering the brain, including the brainstem structures and ventricles, and whole spine.

pituitary gland part of brain
This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by body region and modality. Brain CT head: non-contrast axial CT head: non-contrast coronal CT head: non-contrast sagittal CT head: non-contrast axial with clinical questions CT.

Axial View Of A Head Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Of Pineal Gland Calcification In The Very
This chapter provides an atlas of neuroanatomy and a discussion of the principles of brain imaging and interpretation. Brain anatomy is shown on 3-T MR T2-weighted images in axial plane (Figs. 2.1 to 2.8), on 3-T MR T1-weighted images in coronal plane (Figs. 2.9 to 2.16), and on 3-T MR T1-weighted images in sagittal plane (Figs. 2.17 and 2.18).

Functional Brain Anatomy Radiology Key
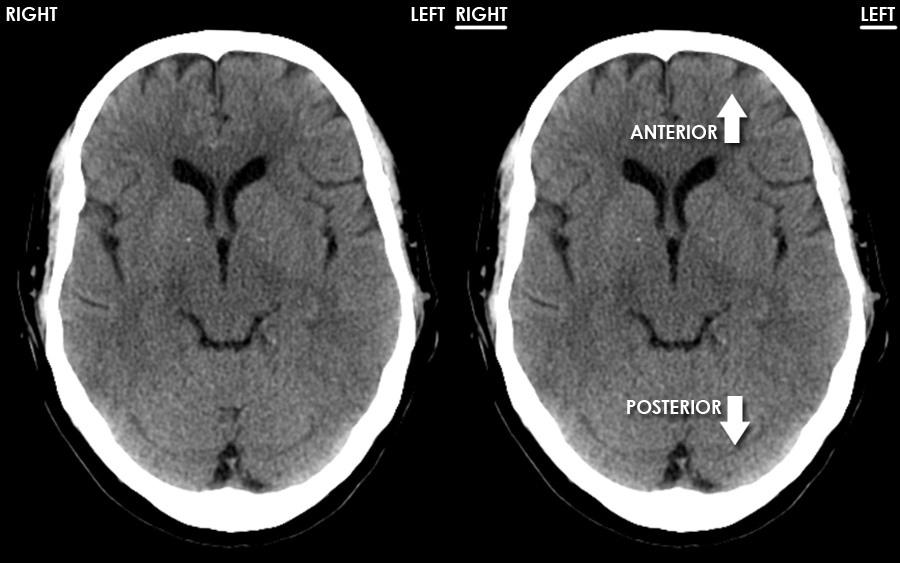
This tutorial takes you through the important anatomy required to understand CT images of the brain. Tutorial orientation. CT images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. This means that the right side of the brain is on the left side of the viewer.
